Gout
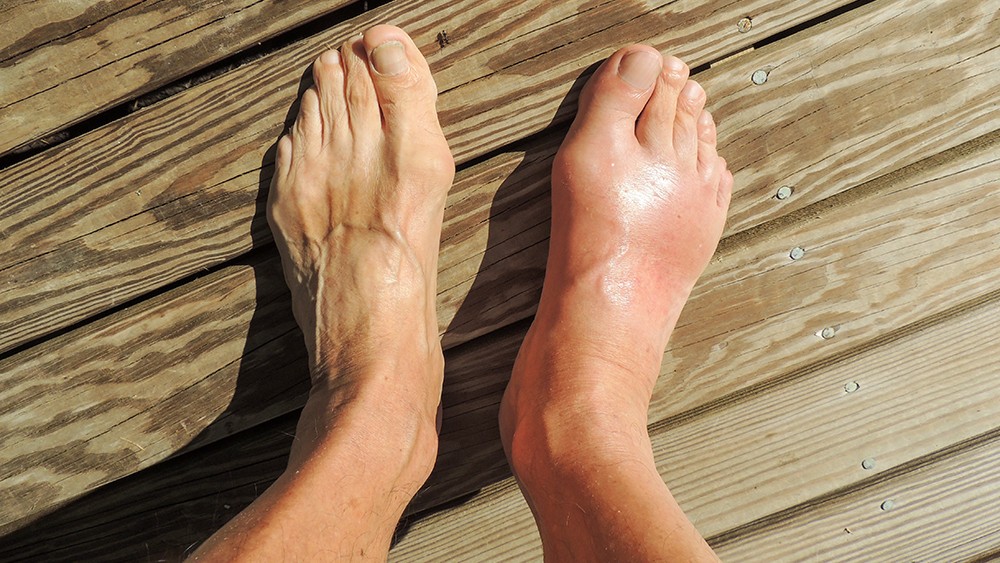
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that occurs when there is a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. The condition most commonly affects the big toe joint, but it can also occur in other joints in the foot and ankle. Gout attacks can be sudden and severe, causing intense pain and swelling in the affected joint. Proper diagnosis and management of gout are essential for managing symptoms and preventing long-term complications.
Causes of Gout
Gout is caused by a buildup of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted by the kidneys. When the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys are not functioning properly, uric acid can build up in the blood and form crystals that can accumulate in the joints. Certain factors can increase the risk of developing gout, including:
- Family history of gout
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Certain medications, such as diuretics or low-dose aspirin
Symptoms of Gout
Symptoms of gout may include:
- Sudden and severe pain in the affected joint, often at night or in the early morning
- Swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the affected joint
- Tenderness and sensitivity to touch in the affected joint
- Flare-ups that last several days to weeks
Diagnosis and Treatment of Gout
Diagnosis of gout typically involves a physical exam, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays or joint aspiration to assess the presence of uric acid crystals in the affected joint. Treatment of gout may involve lifestyle modifications such as weight loss and a low-purine diet to reduce the production of uric acid. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, or corticosteroids may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation during flare-ups. Long-term management of gout may involve medications such as uric acid-lowering drugs to prevent future flare-ups.
Preventing Gout
Preventing gout can be achieved by taking the following precautions:
- Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity
- Avoiding foods that are high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol
- Staying hydrated and drinking plenty of fluids
- Managing underlying medical conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes
- Following a medication regimen as prescribed by a healthcare professional
If you suspect that you have gout or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to seek the care and treatment from Team AFFC who specializes in foot and ankle care. Early diagnosis and proper management of gout can help manage symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
